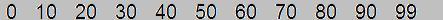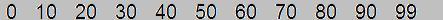IPIP-NEO Report for Fabián
NOTE: The report sent to your computer screen upon the completion of the IPIP-NEO is only a temporary web page. When you exit your web browser you will not be able to return to this URL to re-access your report. No copies of the report are sent to anyone. IF YOU WANT A PERMANENT COPY OF THE REPORT, YOU MUST SAVE THE WEB PAGE TO YOUR HARD DRIVE OR OTHER STORAGE MEDIUM, AND/OR PRINT THE REPORT WHILE YOU ARE STILL VIEWING IT IN YOUR WEB BROWSER. Probably the best way to save the report is to select and copy the entire page (Ctrl-A, Ctrl-C on most browsers), paste it into a word processor, and save the document.
This report compares Fabián from the country Spain to average scores from 720,288 persons of all genders, ages, and nationalities.. (The name used in this report is either a nickname chosen by the person taking the test, or, if a valid nickname was not chosen, a random nickname generated by the program.)
This report estimates the individual's level on each of the five broad personality domains of the Five-Factor Model. The description of each one of the five broad domains is followed by a more detailed description of personality according to the six subdomains that comprise each domain.
A note on terminology. Personality traits describe, relative to other people, the frequency or intensity of a person's feelings, thoughts, or behaviors. Possession of a trait is therefore a matter of degree. We might describe two individuals as extraverts, but still see one as more extraverted than the other. This report uses expressions such as "extravert" or "high in extraversion" to describe someone who is likely to be seen by others as relatively extraverted. The computer program that generates this report classifies you as low, average, or high in a trait according to whether your score is approximately in the lowest 30%, middle 40%, or highest 30% of scores obtained by people of your sex and roughly your age. Your numerical scores are reported and graphed as percentile estimates. For example, a score of "60" means that your level on that trait is estimated to be higher than 60% of persons of your sex and age.
Please keep in mind that "low," "average," and "high" scores on a personality test are neither absolutely good nor bad. A particular level on any trait will probably be neutral or irrelevant for a great many activites, be helpful for accomplishing some things, and detrimental for accomplishing other things.
As with any personality inventory, scores and descriptions can only approximate an individual's actual personality. High and low score descriptions are usually accurate, but average scores close to the low or high boundaries might misclassify you as only average. On each set of six subdomain scales it is somewhat uncommon but certainly possible to score high in some of the subdomains and low in the others. In such cases more attention should be paid to the subdomain scores than to the broad domain score. Questions about the accuracy of your results are best resolved by showing your report to people who know you well.
John A. Johnson wrote descriptions of the five domains and thirty subdomains. These descriptions are based on an extensive reading of the scientific literature on personality measurement. Although Dr. Johnson would like to be acknowledged as the author of these materials if they are reproduced, he has placed them in the public domain.
Extraversion
Extraversion is marked by pronounced engagement with the external world. Extraverts enjoy being with people, are full of energy, and often experience
positive emotions. They tend to be enthusiastic, action-oriented, individuals who are likely to say "Yes!" or "Let's go!" to opportunities for excitement.
In groups they like to talk, assert themselves, and draw attention to
themselves.
Introverts lack the exuberance, energy, and activity levels of extraverts. They tend to be quiet, low-key, deliberate, and disengaged from the social world. Their lack of social involvement should not be interpreted as shyness or depression; the introvert simply needs less stimulation than an extravert and prefers to be alone. The independence and reserve of the introvert is sometimes mistaken as unfriendliness or arrogance. In reality, an introvert who scores high on the agreeableness dimension will not seek others out but will be quite pleasant when approached.
| DOMAIN/Facet | Score | 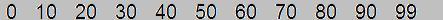 |
| EXTRAVERSION | 1 |  |
| ..Friendliness | 1 |  |
| ..Gregariousness | 1 |  |
| ..Assertiveness | 2 |  |
| ..Activity Level | 42 |  |
| ..Excitement-Seeking | 1 |  |
| ..Cheerfulness | 2 |  |
Your score on Extraversion is low, indicating you are introverted, reserved, and quiet. You enjoy solitude and solitary activities. Your socializing tends to be restricted to a few close friends.
Extraversion Facets
- Friendliness. Friendly people genuinely like other people and openly
demonstrate positive feelings toward others. They make friends quickly
and it is easy for them to form close, intimate relationships. Low scorers
on Friendliness are not necessarily cold and hostile, but they do not reach
out to others and are perceived as distant and reserved. Your level of
friendliness is low.
- Gregariousness. Gregarious people find the company of others
pleasantly stimulating and rewarding. They enjoy the excitement of
crowds. Low scorers tend to feel overwhelmed by, and therefore actively
avoid, large crowds. They do not necessarily dislike being with people
sometimes, but their need for privacy and time to themselves is much
greater than for individuals who score high on this scale. Your level of
gregariousness is low.
- Assertiveness. High scorers Assertiveness like to speak out, take
charge, and direct the activities of others. They tend to be leaders in
groups. Low scorers tend not to talk much and let others control the
activities of groups. Your level of assertiveness is low.
- Activity Level. Active individuals lead fast-paced, busy lives. They
move about quickly, energetically, and vigorously, and they are involved in
many activities. People who score low on this scale follow a slower and
more leisurely, relaxed pace. Your activity level is average.
- Excitement-Seeking. High scorers on this scale are easily bored
without high levels of stimulation. They love bright lights and hustle and
bustle. They are likely to take risks and seek thrills. Low scorers are
overwhelmed by noise and commotion and are adverse to thrill-seeking.
Your level of excitement-seeking is low.
- Cheerfulness. This scale measures positive mood and feelings, not
negative emotions (which are a part of the Neuroticism domain). Persons who
score high on this scale typically experience a range of positive feelings,
including happiness, enthusiasm, optimism, and joy. Low scorers are not as
prone to such energetic, high spirits. Your level of positive emotions is
low.
Agreeableness
Agreeableness reflects individual differences in concern with cooperation and
social harmony. Agreeable individuals value getting along with others. They are
therefore considerate, friendly, generous, helpful, and willing to compromise
their interests with others'. Agreeable people also have an optimistic view of
human nature. They believe people are basically honest, decent, and
trustworthy.
Disagreeable individuals place self-interest above getting along with others.
They are generally unconcerned with others' well-being, and therefore are
unlikely to extend themselves for other people. Sometimes their skepticism about
others' motives causes them to be suspicious, unfriendly, and
uncooperative.
Agreeableness is obviously advantageous for attaining and maintaining
popularity. Agreeable people are better liked than disagreeable people. On the
other hand, agreeableness is not useful in situations that require tough or
absolute objective decisions. Disagreeable people can make excellent scientists,
critics, or soldiers.
| DOMAIN/Facet | Score | 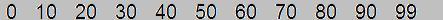 |
| AGREEABLENESS | 63 |  |
| ..Trust | 40 |  |
| ..Morality | 93 |  |
| ..Altruism | 11 |  |
| ..Cooperation | 73 |  |
| ..Modesty | 42 |  |
| ..Sympathy | 87 |  |
Your level of Agreeableness is average, indicating some concern with others'
Needs, but, generally, unwillingness to sacrifice yourself for others.
Agreeableness Facets
- Trust. A person with high trust assumes that most people are
fair, honest, and have good intentions. Persons low in trust see others
as selfish, devious, and potentially dangerous. Your level of
trust is average.
- Morality. High scorers on this scale see no need for pretense
or manipulation when dealing with others and are therefore candid, frank,
and sincere. Low scorers believe that a certain amount of deception in
social relationships is necessary. People find it relatively easy to relate
to the straightforward high-scorers on this scale. They generally find it
more difficult to relate to the unstraightforward low-scorers on this
scale. It should be made clear that low scorers are not unprincipled
or immoral; they are simply more guarded and less willing to openly reveal
the whole truth. Your level of morality is high.
- Altruism. Altruistic people find helping other people genuinely
rewarding. Consequently, they are generally willing to assist those who
are in need. Altruistic people find that doing things for others is a form
of self-fulfillment rather than self-sacrifice. Low scorers on this scale
do not particularly like helping those in need. Requests for help feel like
an imposition rather than an opportunity for self-fulfillment. Your level
of altruism is low.
- Cooperation. Individuals who score high on this scale dislike
confrontations. They are perfectly willing to compromise or to deny their
own needs in order to get along with others. Those who score low on this
scale are more likely to intimidate others to get their way. Your
level of compliance is high.
- Modesty. High scorers on this scale do not like to claim that they
are better than other people. In some cases this attitude may derive from
low self-confidence or self-esteem. Nonetheless, some people with high
self-esteem find immodesty unseemly. Those who are willing to
describe themselves as superior tend to be seen as disagreeably arrogant
by other people. Your level of modesty is average.
- Sympathy. People who score high on this scale are tenderhearted
and compassionate. They feel the pain of others vicariously and are easily
moved to pity. Low scorers are not affected strongly by human suffering.
They pride themselves on making objective judgments based on reason.
They are more concerned with truth and impartial justice than with mercy.
Your level of tender-mindedness is high.
Conscientiousness
Conscientiousness concerns the way in which we control, regulate, and direct our impulses. Impulses are not inherently bad; occasionally time constraints require a snap decision, and acting on our first impulse can be an effective response. Also, in times of play rather than work, acting spontaneously and impulsively can be fun. Impulsive individuals can be seen by others as colorful, fun-to-be-with, and zany.
Nonetheless, acting on impulse can lead to trouble in a number of ways. Some impulses are antisocial. Uncontrolled antisocial acts not only harm other members of society, but also can result in retribution toward the perpetrator of such impulsive acts. Another problem with impulsive acts is that they often produce immediate rewards but undesirable, long-term consequences. Examples include excessive socializing that leads to being fired from one's job, hurling an insult that causes the breakup of an important relationship, or using pleasure-inducing drugs that eventually destroy one's health.
Impulsive behavior, even when not seriously destructive, diminishes a person's effectiveness in significant ways. Acting impulsively disallows contemplating alternative courses of action, some of which would have been wiser than the impulsive choice. Impulsivity also sidetracks people during projects that require organized sequences of steps or stages. Accomplishments of an impulsive person are therefore small, scattered, and inconsistent.
A hallmark of intelligence, what potentially separates human beings from earlier life forms, is the ability to think about future consequences before acting on an impulse. Intelligent activity involves contemplation of long-range goals, organizing and planning routes to these goals, and persisting toward one's goals in the face of short-lived impulses to the contrary. The idea that intelligence involves impulse control is nicely captured by the term prudence, an alternative label for the Conscientiousness domain. Prudent means both wise and cautious. Persons who score high on the Conscientiousness scale are, in fact, perceived by others as intelligent.
The benefits of high conscientiousness are obvious. Conscientious individuals avoid trouble and achieve high levels of success through purposeful planning and persistence. They are also positively regarded by others as intelligent and reliable. On the negative side, they can be compulsive perfectionists and workaholics. Furthermore, extremely conscientious individuals might be regarded as stuffy and boring. Unconscientious people may be criticized for their unreliability, lack of ambition, and failure to stay within the lines, but they will experience many short-lived pleasures and they will never be called stuffy.
| DOMAIN/Facet | Score |  |
| CONSCIENTIOUSNESS | 63 |  |
| ..Self-Efficacy | 30 |  |
| ..Orderliness | 61 |  |
| ..Dutifulness | 91 |  |
| ..Achievement-Striving | 76 |  |
| ..Self-Discipline | 7 |  |
| ..Cautiousness | 95 |  |
Your score on Conscientiousness is average. This means you are reasonably reliable, organized, and self-controlled.
Conscientiousness Facets
- Self-Efficacy. Self-Efficacy describes confidence in one's ability
to accomplish things. High scorers believe they have the intelligence
(common sense), drive, and self-control necessary for achieving success.
Low scorers do not feel effective, and may have a sense that they are not
in control of their lives. Your level of self-efficacy is low.
- Orderliness. Persons with high scores on orderliness are
well-organized. They like to live according to routines and schedules. They
keep lists and make plans. Low scorers tend to be disorganized and
scattered. Your level of orderliness is average.
- Dutifulness. This scale reflects the strength of a person's sense
of duty and obligation. Those who score high on this scale have a strong
sense of moral obligation. Low scorers find contracts, rules, and
regulations overly confining. They are likely to be seen as unreliable or
even irresponsible. Your level of dutifulness is high.
- Achievement-Striving. Individuals who score high on this
scale strive hard to achieve excellence. Their drive to be recognized as
successful keeps them on track toward their lofty goals. They often have
a strong sense of direction in life, but extremely high scores may
be too single-minded and obsessed with their work. Low scorers are content
to get by with a minimal amount of work, and might be seen by others
as lazy. Your level of achievement striving is high.
- Self-Discipline. Self-discipline-what many people call
will-power-refers to the ability to persist at difficult or unpleasant
tasks until they are completed. People who possess high self-discipline
are able to overcome reluctance to begin tasks and stay on track despite
distractions. Those with low self-discipline procrastinate and show poor
follow-through, often failing to complete tasks-even tasks they want very
much to complete. Your level of self-discipline is low.
- Cautiousness. Cautiousness describes the disposition to
think through possibilities before acting. High scorers on the Cautiousness
scale take their time when making decisions. Low scorers often say or do
first thing that comes to mind without deliberating alternatives and the
probable consequences of those alternatives. Your level
of cautiousness is high.
Neuroticism
Freud originally used the term neurosis to describe a condition marked by mental distress, emotional suffering, and an inability to cope effectively with the normal demands of life. He suggested that everyone shows some signs of neurosis, but that we differ in our degree of suffering and our specific symptoms of distress. Today neuroticism refers to the tendency to experience negative feelings. Those who score high on Neuroticism may experience primarily one specific negative feeling such as anxiety, anger, or depression, but are likely to experience several of these emotions. People high in neuroticism are emotionally reactive. They respond emotionally to events that would not affect most people, and their reactions tend to be more intense than normal. They are more likely to interpret ordinary situations as threatening, and minor frustrations as hopelessly difficult. Their negative emotional reactions tend to persist for unusually long periods of time, which means they are often in a bad mood. These problems in emotional regulation can diminish a neurotic's ability to think clearly, make decisions, and cope effectively with stress.
At the other end of the scale, individuals who score low in neuroticism are less easily upset and are less emotionally reactive. They tend to be calm, emotionally stable, and free from persistent negative feelings. Freedom from negative feelings does not mean that low scorers experience a lot of positive feelings; frequency of positive emotions is a component of the Extraversion domain.
| DOMAIN/Facet | Score |  |
| NEUROTICISM | 69 |  |
| ..Anxiety | 76 |  |
| ..Anger | 8 |  |
| ..Depression | 74 |  |
| ..Self-Consciousness | 99 |  |
| ..Immoderation | 60 |  |
| ..Vulnerability | 47 |  |
Your score on Neuroticism is high, indicating that you are easily upset, even by what most people consider the normal demands of living. People consider you to be sensitive and emotional.
Neuroticism Facets
- Anxiety. The "fight-or-flight" system of the brain of anxious
individuals is too easily and too often engaged. Therefore, people who
are high in anxiety often feel like something dangerous is about to happen.
They may be afraid of specific situations or be just generally fearful.
They feel tense, jittery, and nervous. Persons low in Anxiety are generally
calm and fearless. Your level of anxiety is high.
- Anger. Persons who score high in Anger feel enraged when
things do not go their way. They are sensitive about being treated fairly
and feel resentful and bitter when they feel they are being cheated.
This scale measures the tendency to feel angry; whether or not the
person expresses annoyance and hostility depends on the individual's
level on Agreeableness. Low scorers do not get angry often or easily.
Your level of anger is low.
- Depression. This scale measures the tendency to feel sad, dejected,
and discouraged. High scorers lack energy and have difficult initiating
activities. Low scorers tend to be free from these depressive feelings.
Your level of depression is high.
- Self-Consciousness. Self-conscious individuals are sensitive
about what others think of them. Their concern about rejection and
ridicule cause them to feel shy and uncomfortable abound others. They
are easily embarrassed and often feel ashamed. Their fears that others
will criticize or make fun of them are exaggerated and unrealistic, but
their awkwardness and discomfort may make these fears a self-fulfilling
prophecy. Low scorers, in contrast, do not suffer from the mistaken
impression that everyone is watching and judging them. They do not feel
nervous in social situations. Your level or self-consciousness is
high.
- Immoderation. Immoderate individuals feel strong cravings and
urges that they have have difficulty resisting. They tend to be
oriented toward short-term pleasures and rewards rather than long-
term consequences. Low scorers do not experience strong, irresistible
cravings and consequently do not find themselves tempted to overindulge.
Your level of immoderation is average.
- Vulnerability. High scorers on Vulnerability experience panic,
confusion, and helplessness when under pressure or stress. Low scorers
feel more poised, confident, and clear-thinking when stressed.
Your level of vulnerability is average.
Openness to Experience
Openness to Experience describes a dimension of cognitive style that
distinguishes imaginative, creative people from down-to-earth, conventional
people. Open people are intellectually curious, appreciative of art, and
sensitive to beauty. They tend to be, compared to closed people, more aware of
their feelings. They tend to think and act in individualistic and nonconforming
ways. Intellectuals typically score high on Openness to Experience;
consequently, this factor has also been called Culture or
Intellect. Nonetheless, Intellect is probably best regarded as one aspect of openness
to experience. Scores on Openness to Experience are only modestly
related to years of education and scores on standard intelligent tests.
Another characteristic of the open cognitive style is a facility for thinking
in symbols and abstractions far removed from concrete experience. Depending on
the individual's specific intellectual abilities, this symbolic cognition may
take the form of mathematical, logical, or geometric thinking, artistic and
metaphorical use of language, music composition or performance, or one of the
many visual or performing arts.
People with low scores on openness to experience tend to have narrow, common
interests. They prefer the plain, straightforward, and obvious over the
complex, ambiguous, and subtle. They may regard the arts and sciences with
suspicion, regarding these endeavors as abstruse or of no practical use.
Closed people prefer familiarity over novelty; they are conservative and
resistant to change.
Openness is often presented as healthier or more mature by psychologists, who
are often themselves open to experience. However, open and closed styles of
thinking are useful in different environments. The intellectual style of the
open person may serve a professor well, but research has shown that closed
thinking is related to superior job performance in police work, sales, and
a number of service occupations.
| DOMAIN/Facet | Score |  |
| OPENNESS | 58 |  |
| ..Imagination | 64 |  |
| ..Artistic Interests | 66 |  |
| ..Emotionality | 79 |  |
| ..Adventurousness | 7 |  |
| ..Intellect | 76 |  |
| ..Liberalism | 40 |  |
Your score on Openness to Experience is average, indicating you enjoy tradition
but are willing to try new things. Your thinking is neither simple nor
complex. To others you appear to be a well-educated person but not an intellectual.
Openness Facets
- Imagination. To imaginative individuals, the real world is
often too plain and ordinary. High scorers on this scale use fantasy as a
way of creating a richer, more interesting world. Low scorers are on this
scale are more oriented to facts than fantasy. Your level of imagination
is average.
- Artistic Interests. High scorers on this scale love beauty, both in
art and in nature. They become easily involved and absorbed in artistic
and natural events. They are not necessarily artistically trained nor
talented, although many will be. The defining features of this scale are
interest in, and appreciation of natural and
artificial beauty. Low scorers lack aesthetic sensitivity and interest in
the arts. Your level of artistic interests is average.
- Emotionality. Persons high on Emotionality have good access
to and awareness of their own feelings. Low scorers are less aware of
their feelings and tend not to express their emotions openly. Your
level of emotionality is high.
- Adventurousness. High scorers on adventurousness are eager to
try new activities, travel to foreign lands, and experience different
things. They find familiarity and routine boring, and will take a new
route home just because it is different. Low scorers tend to feel
uncomfortable with change and prefer familiar routines. Your level of
adventurousness is low.
- Intellect. Intellect and artistic interests are the two most
important, central aspects of openness to experience. High scorers on
Intellect love to play with ideas. They are open-minded to new and unusual
ideas, and like to debate intellectual issues. They enjoy riddles, puzzles,
and brain teasers. Low scorers on Intellect prefer dealing with either
people or things rather than ideas. They regard intellectual exercises as a
waste of time. Intellect should not be equated with intelligence.
Intellect is an intellectual style, not an intellectual ability, although
high scorers on Intellect score slightly higher than low-Intellect
individuals on standardized intelligence tests. Your level of intellect
is high.
- Liberalism. Psychological liberalism refers to a readiness to
challenge authority, convention, and traditional values. In its most
extreme form, psychological liberalism can even represent outright
hostility toward rules, sympathy for law-breakers, and love of ambiguity,
chaos, and disorder. Psychological conservatives prefer the security and
stability brought by conformity to tradition. Psychological liberalism
and conservatism are not identical to political affiliation, but certainly
incline individuals toward certain political parties. Your level of
liberalism is average.